HHO Bulgaria
» Иновативни
Водородни Технологии
Български производител на
Водородно оборудване
за Здравето, Бита и Бизнеса

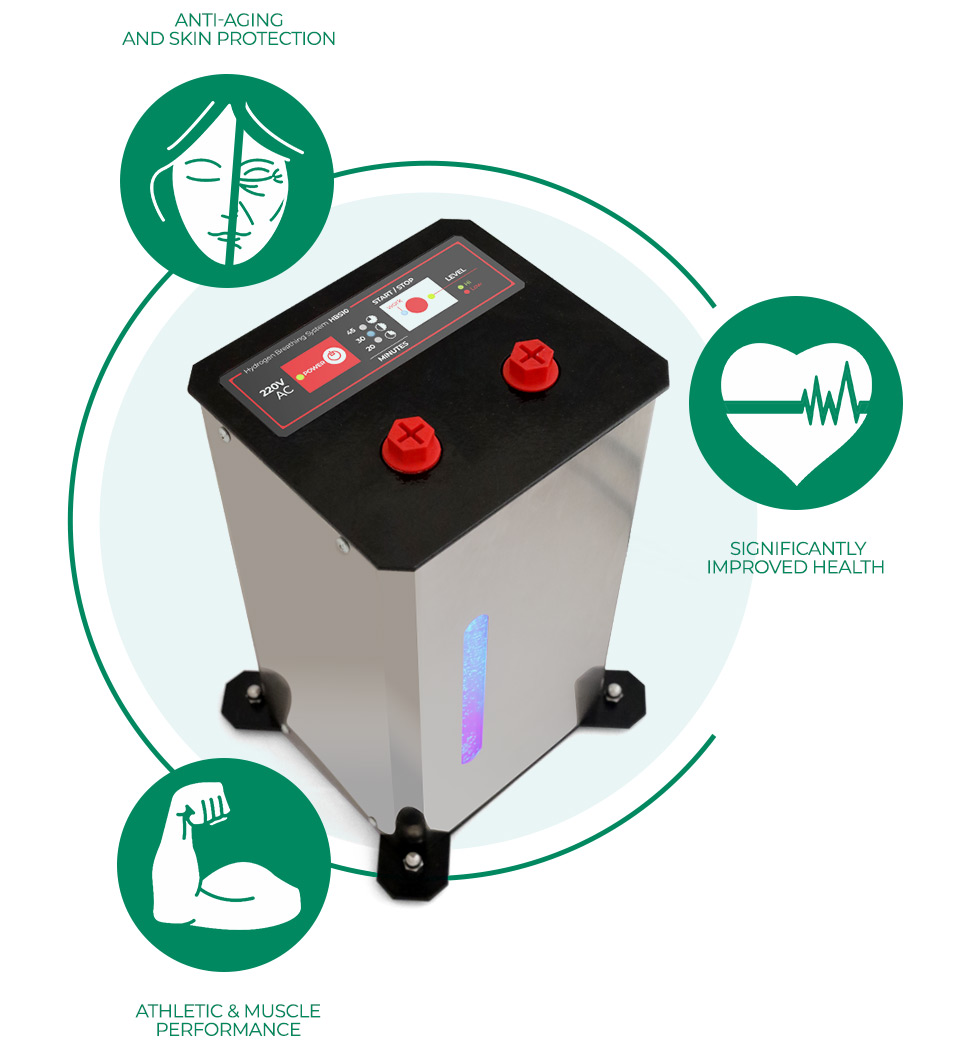
Апарати за Водородна Терапия
» Здраве
Стотици научни публикации доказват, че водородът ефективно подпомага човешкия организъм в борбата с вирусни инфекции, както и предотвратява образуването на свободни радикали и ракови клетки в тялото.
Вече над 10 години нашите устройства за Водородна Терапия помагат на хора по цял свят да се грижат за своите Здраве, Жизненост и Красота по един напълно Безопасен, Безболезнен и Натурален начин!
Топ Апарат:

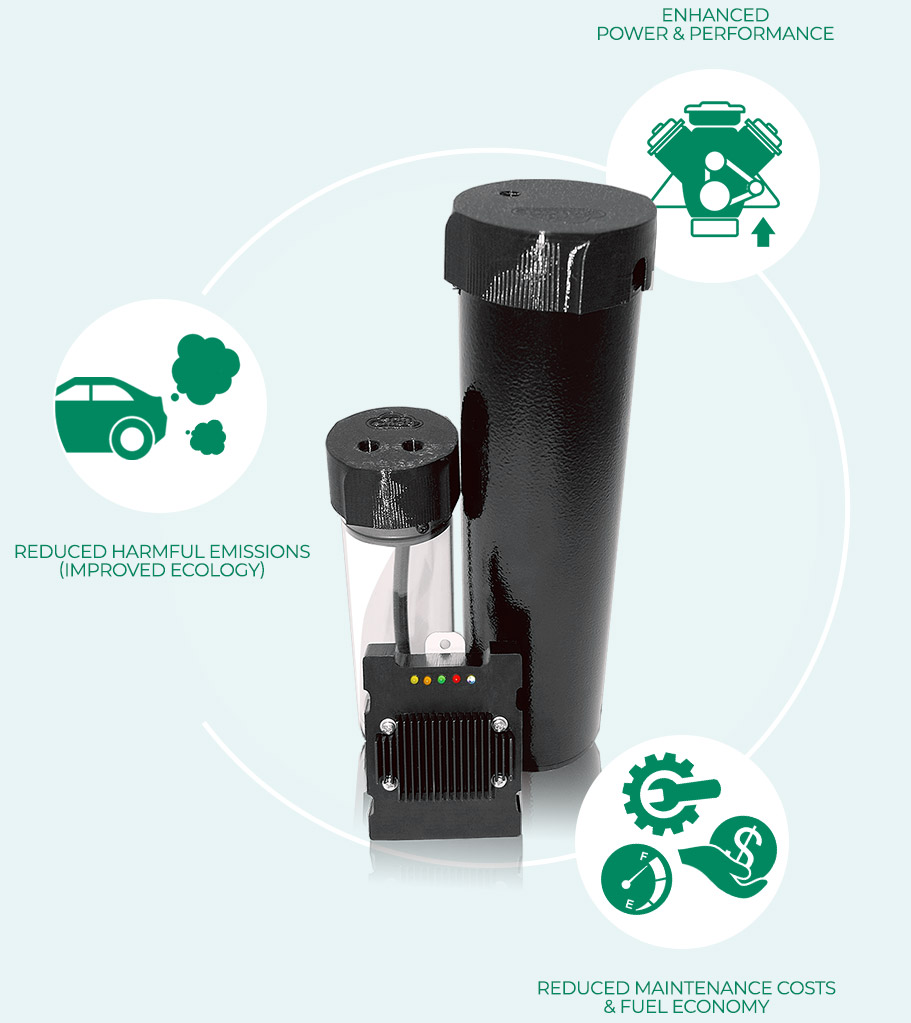
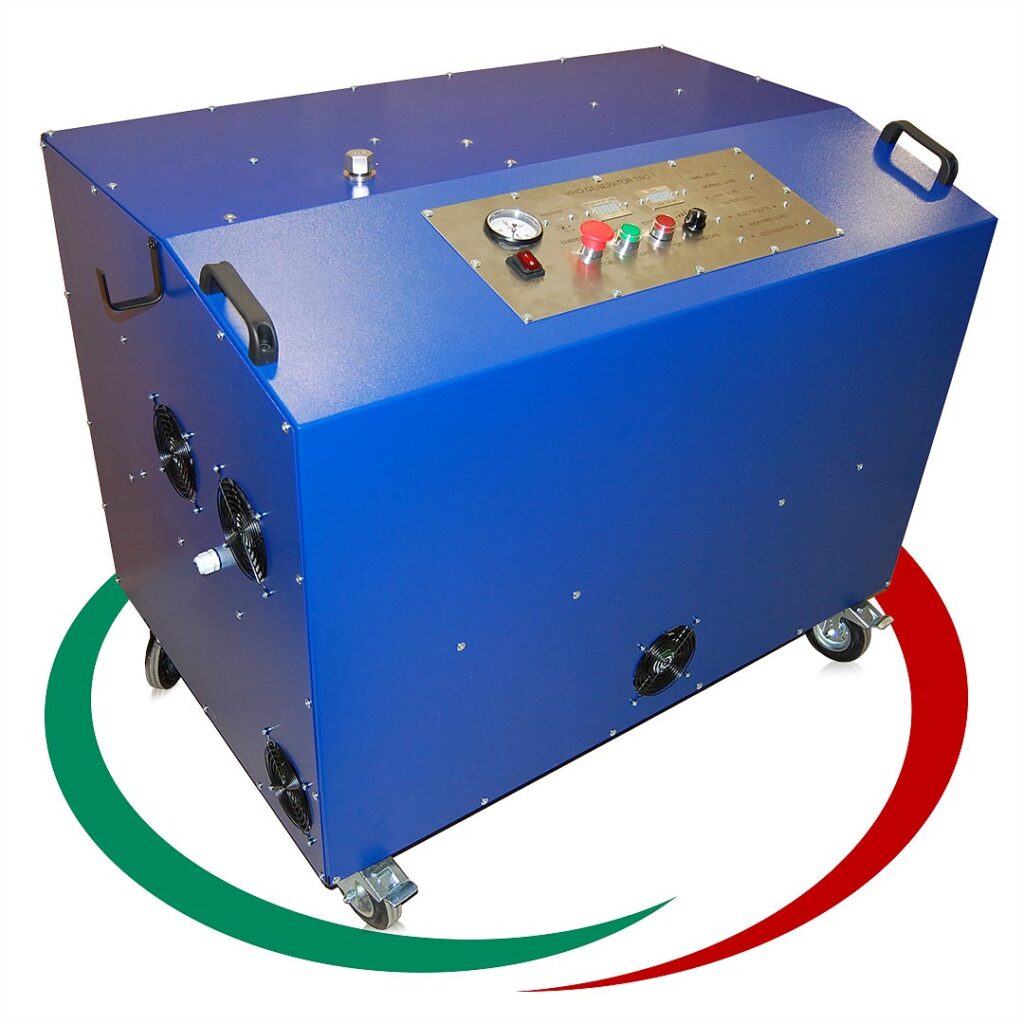
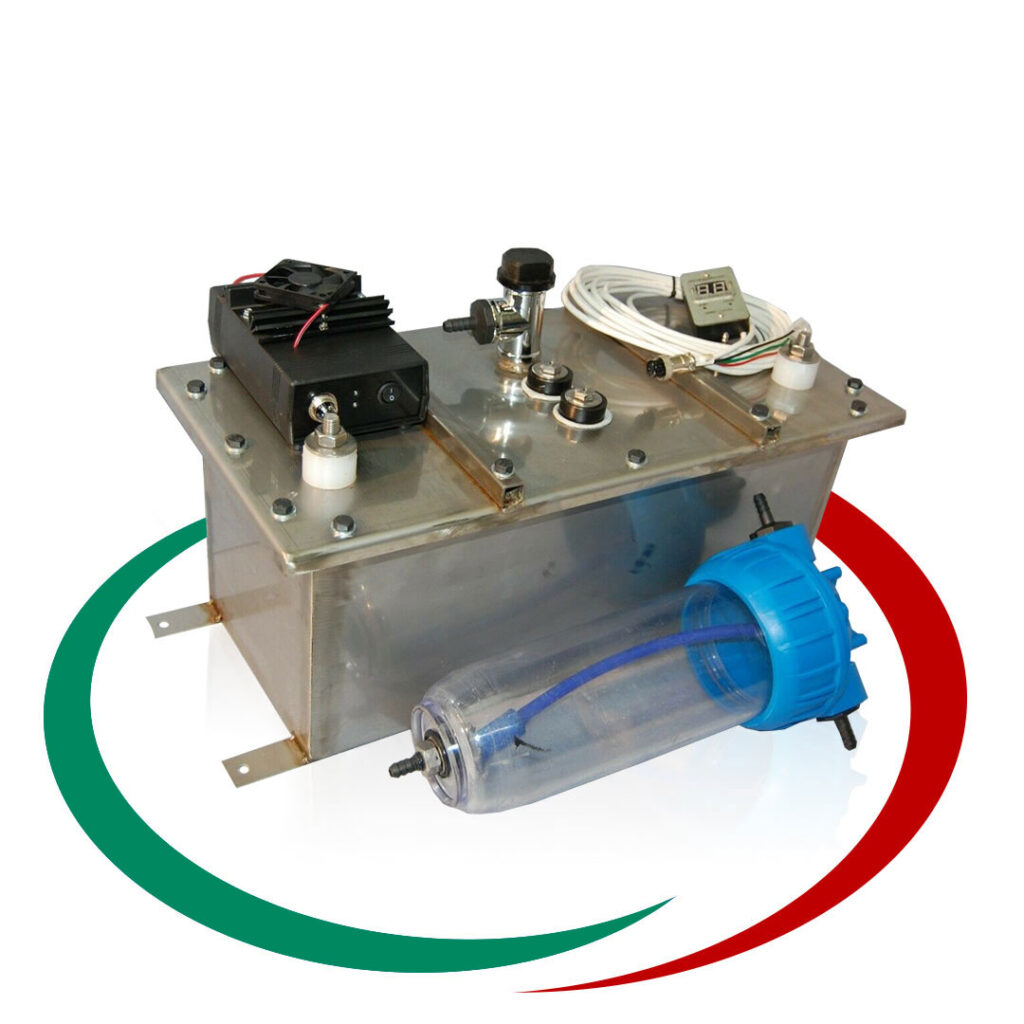
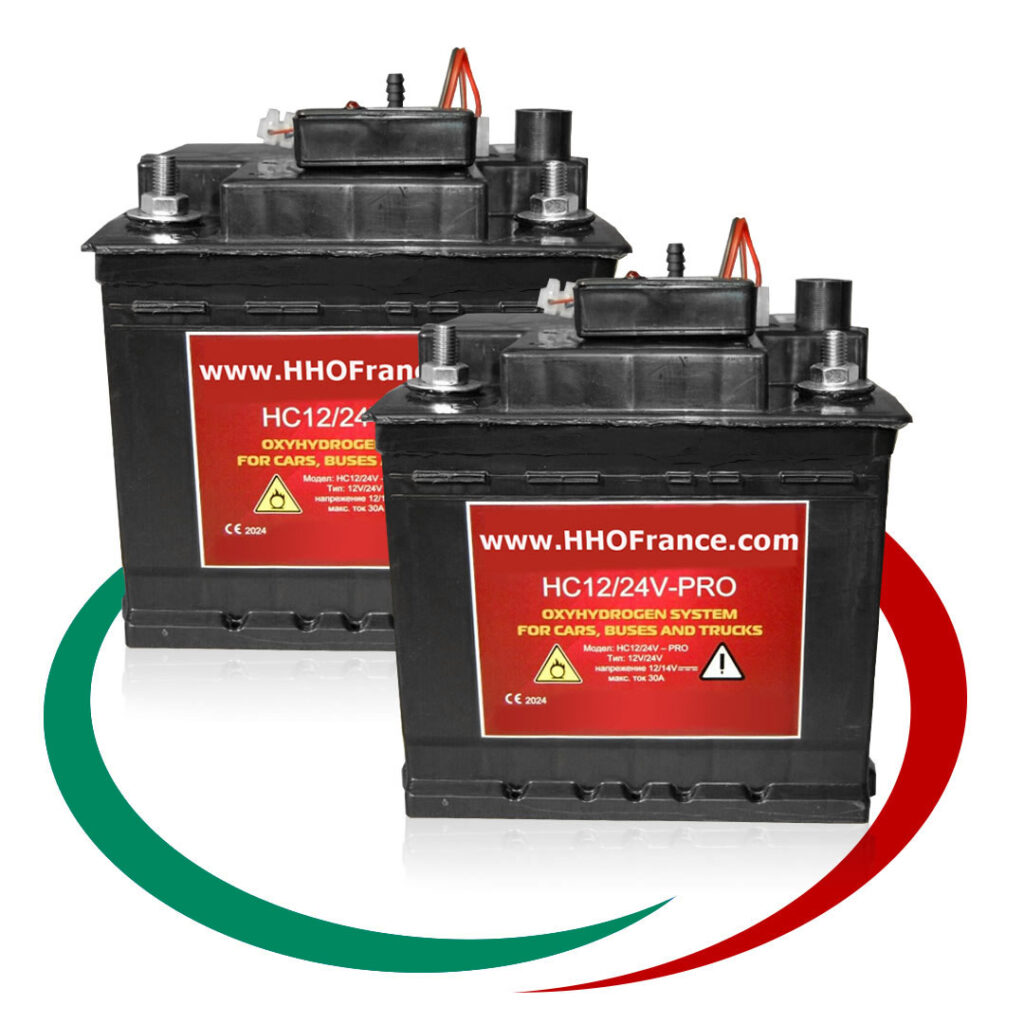
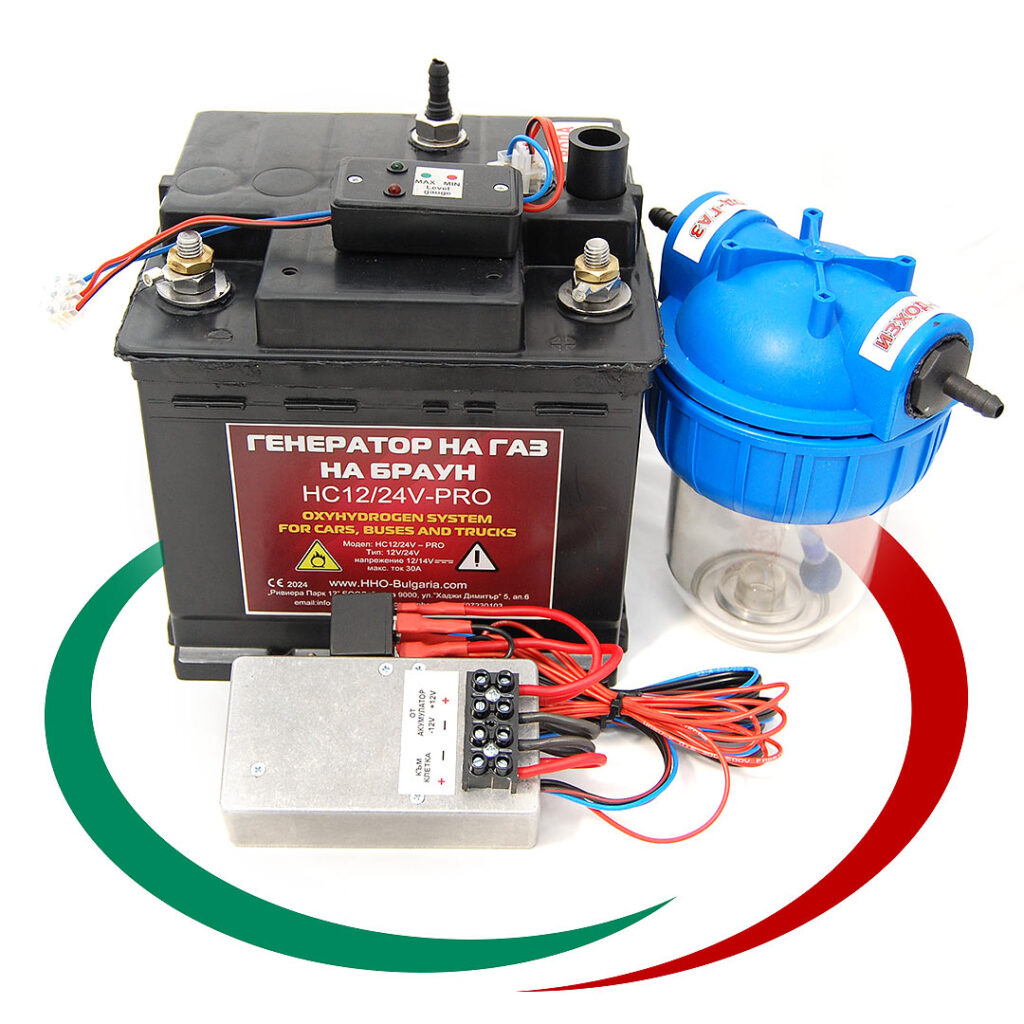
HHO Генератори
» Автомобили
Нашите Водородни Генератори доказано повишават екологичността и мощността на двигателя, спомагат за реализиране икономия на гориво и чувствително редуцират разходите за цялостната поддръжка на автомобила.
Икономия, Екология и Бизнес:
Най-продавани Водородни Генератори:

HHO Bulgaria
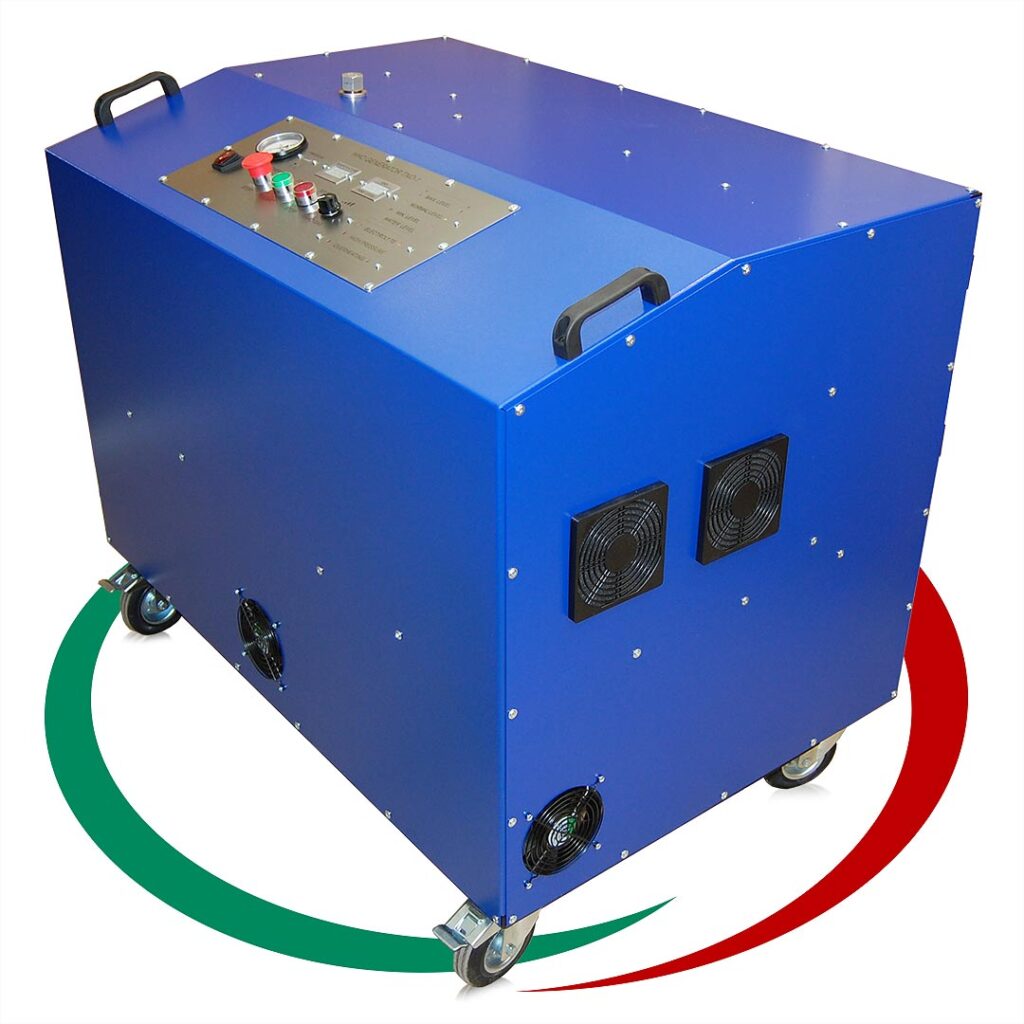
Оборудване за
Бизнеса и Промишлеността


Зеленият Водород е възобновяем екологично чист източник на енергия, който се получава при електролиза на вода, като електричеството за неговото производство се осигурява от други възобновяеми енергийни източници.
Това е Бъдещето на Водородните Технологии и ние сме горди да бъдем част от него!
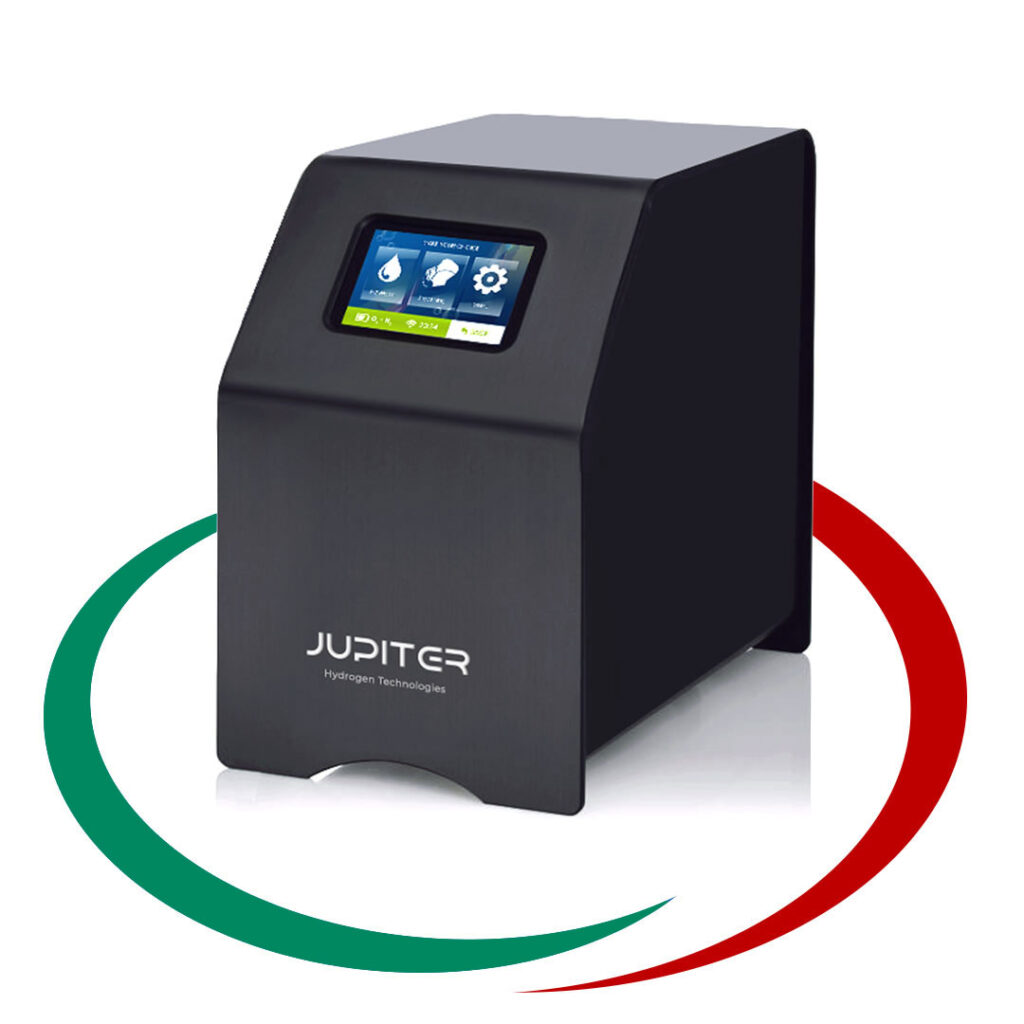
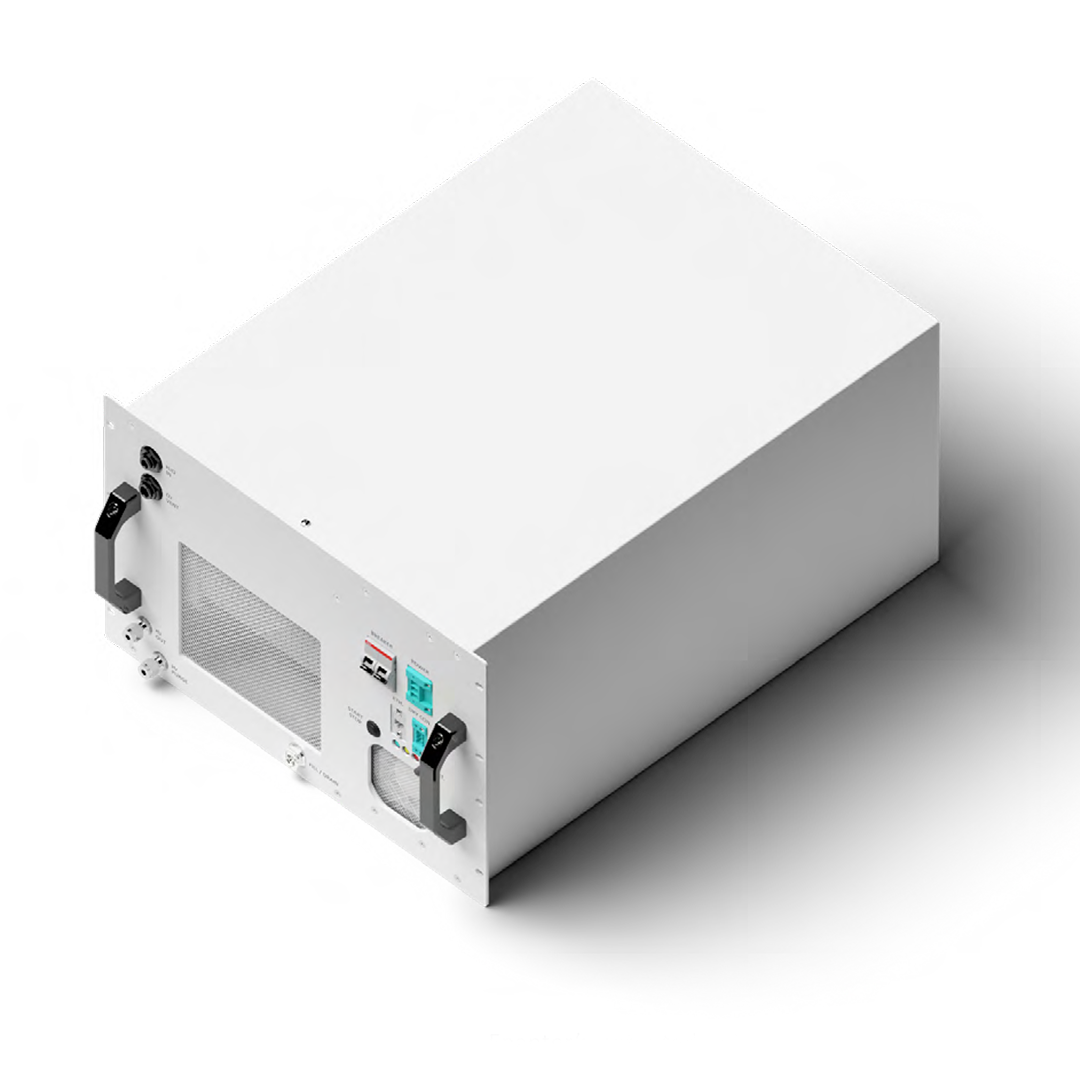
Електролизер
EL 4
Plug & Play AEM електролизер, който повишава ефективността на възобновяемото електричество, преобразувайки го в евтин Зелен Водород.

НОВО
За първи път в България водородно почистване на нагари на ДВГ цена 18 лв. на цилиндър
Обадете се сега на 0878 21 78 10 и запазете час!
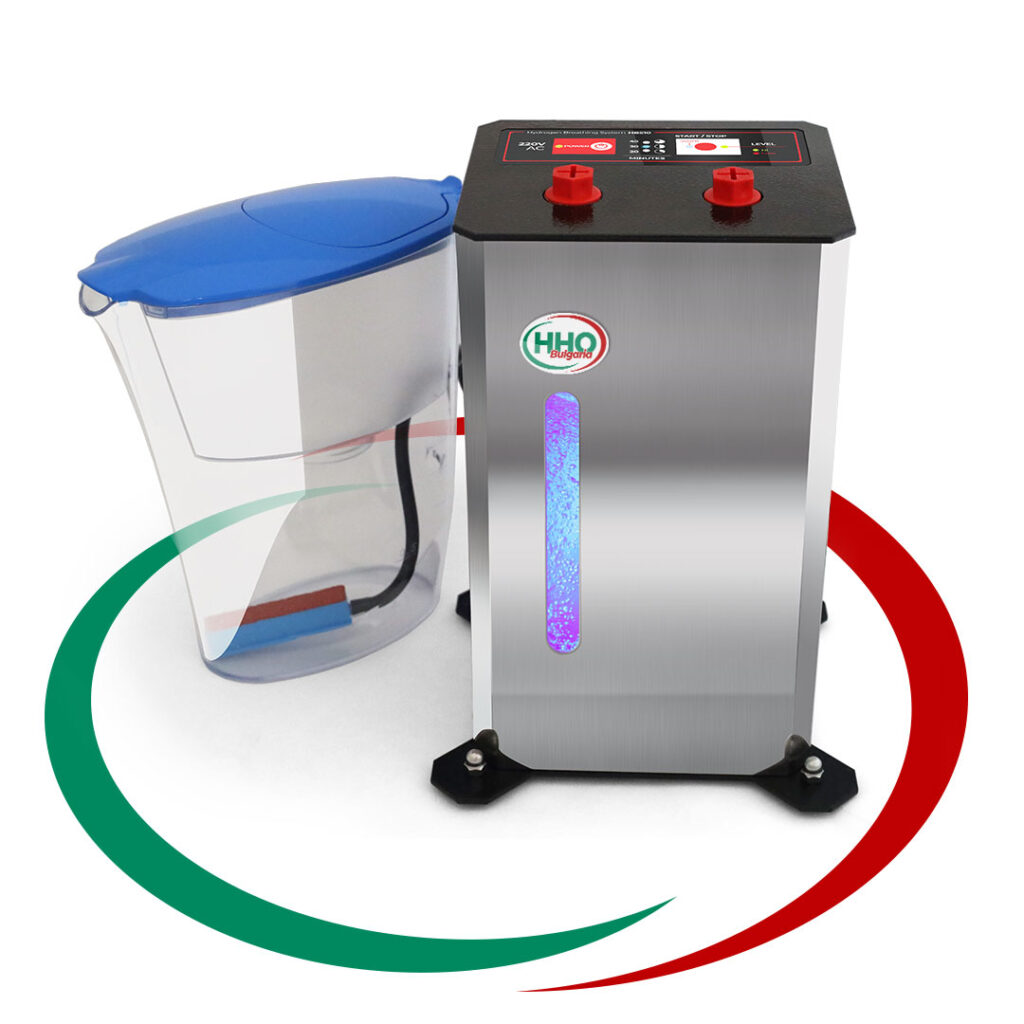
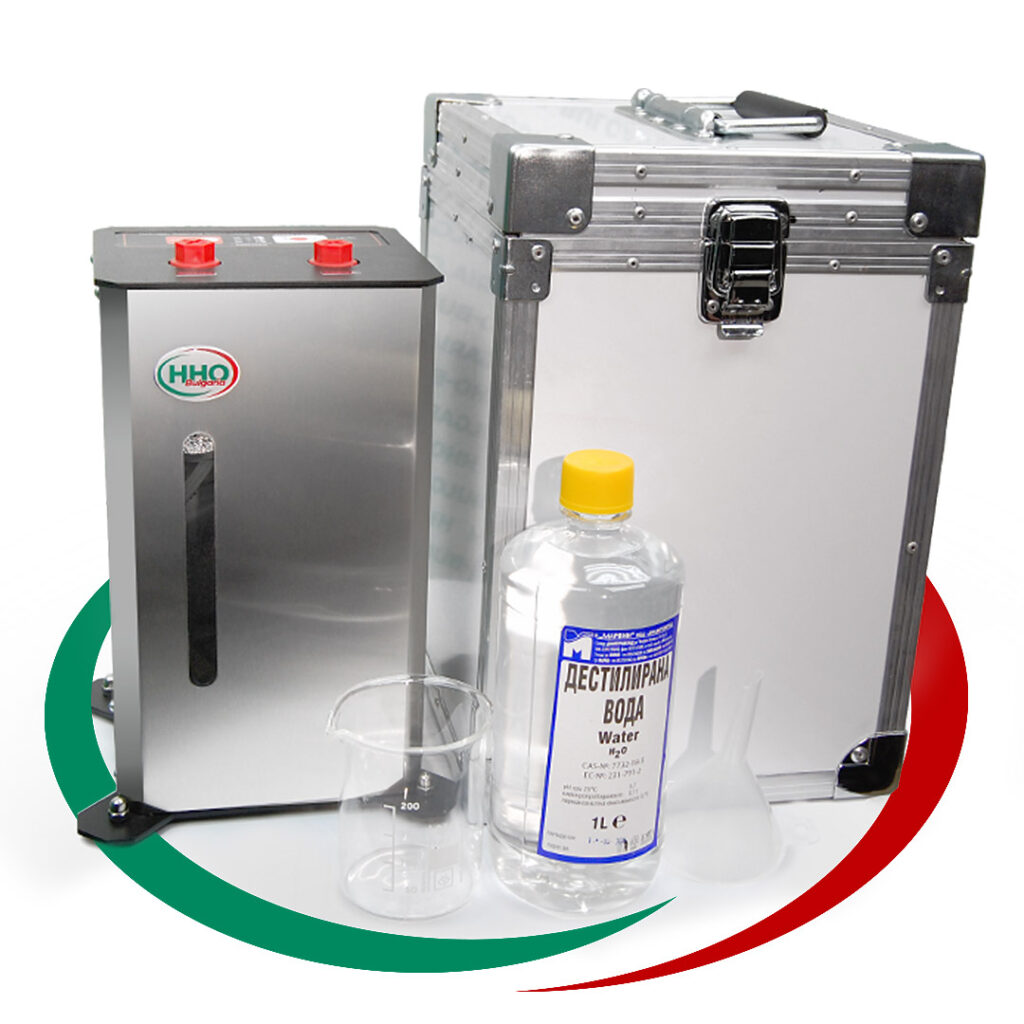
Водородна
Терапия
Апарати за Водородна Вода и
Инхалации с Водород
Браунов Газ
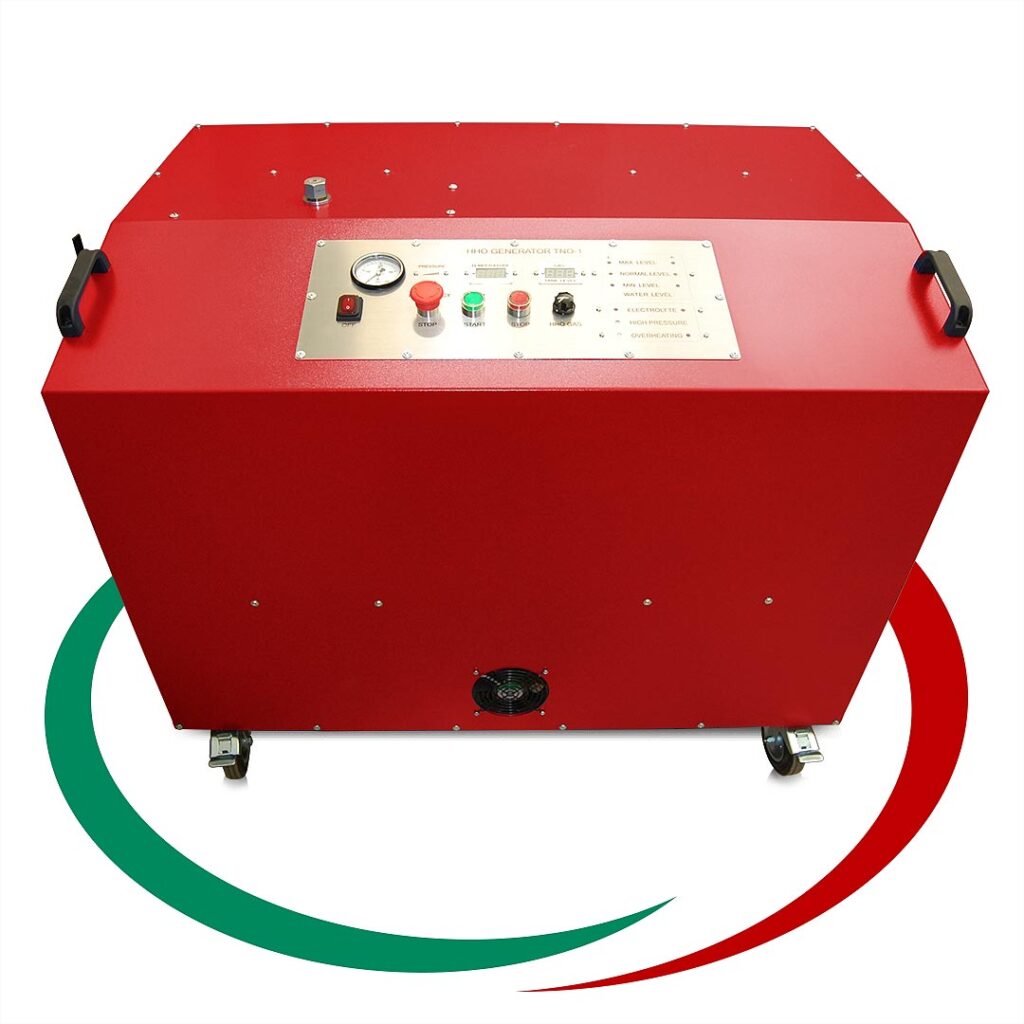
Избрано от категория “HHO Генератори”
Генераторът на Газ на Браун ( HHO газ ) или като е популярен в България „Водороден генератор”, се използва за производството на газ, който се явява добавка към горивото, ускоряваща процеса на изгаряне на гориво-въздушната смес в цилиндрите на двигателя. Получения ефект от по-доброто изгаряне е повишаване на мощността на двигателя и значителна икономия на гориво. Възможно е увеличаване пробега с до 50% със същото количество гориво. Водородния генератор (HHO генератора) е предназначен за всякакъв вид ДВГ работещи с бензин, дизел, пропан-бутан или метан.
HHO-Bulgaria.com
(други акценти от сайта)
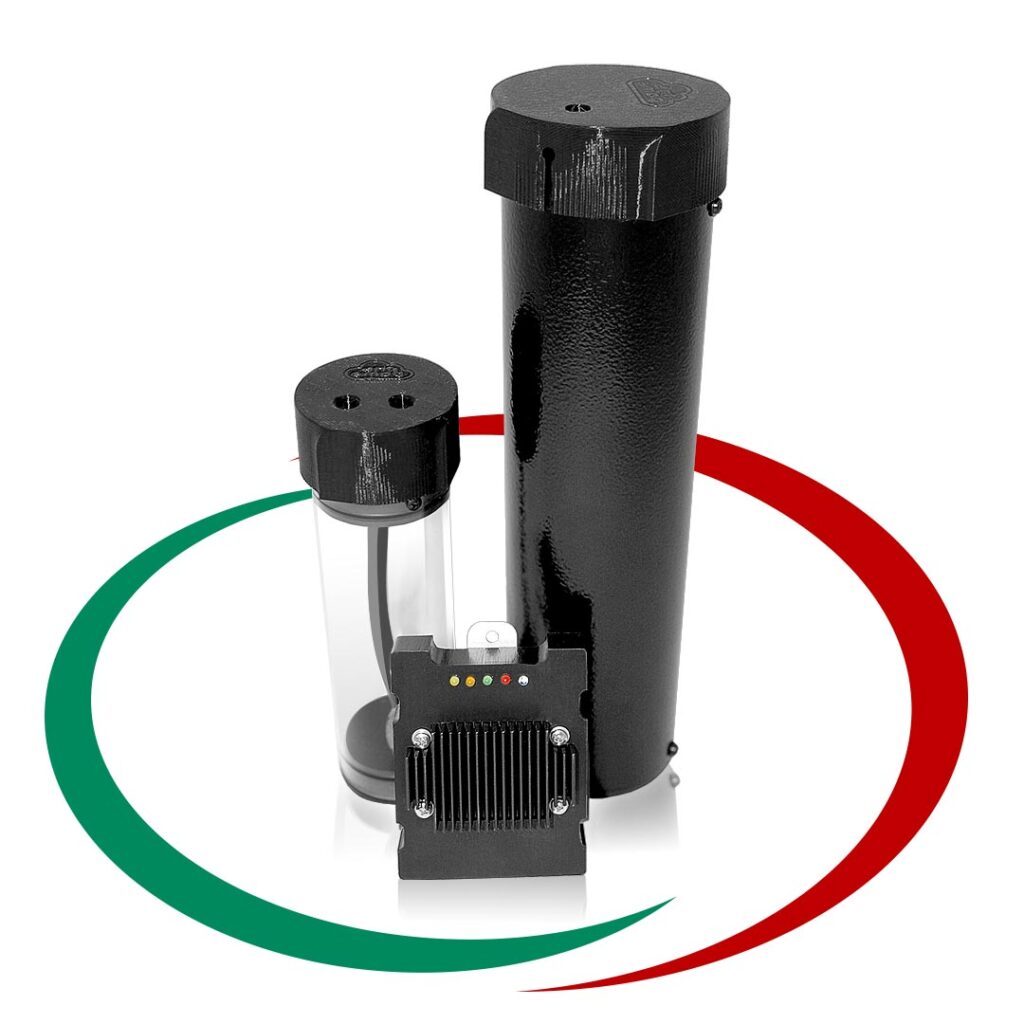
НОВО Апарат за дишане на водород и насищане на вода с водорд.
Особенно ефективен при заболели с корона вирус, пневмония и други. Водорода е най силния антиоксидант. Положителното му въздействие на човешкия организъм и методите за терапия са описани в много научни статии, някой от които може да прочетете на нашия сайт в меню “ЗДРАВЕ”…
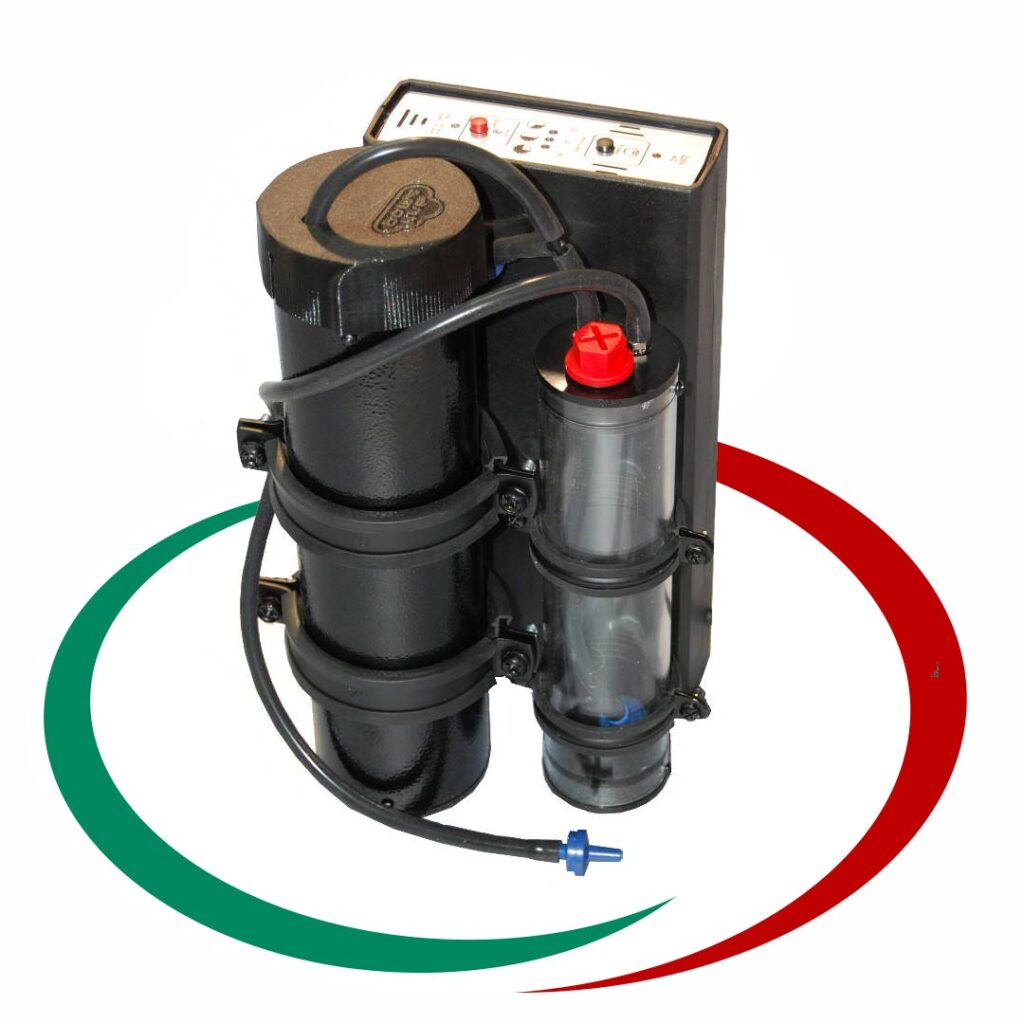
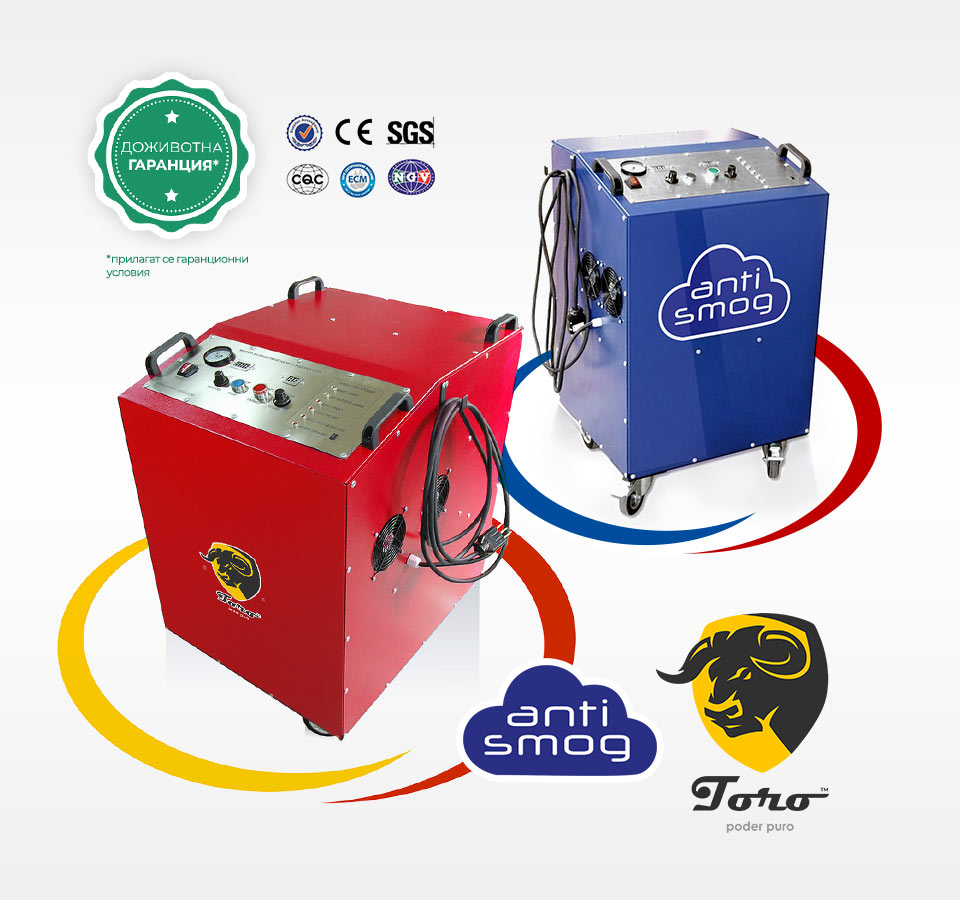
Апарат за водородно почистване на нагари в ДВГ, DPF, EGR, цилиндър, бутало и др.
Ние сме производители на апарати за водородно почистване от 10 години. Апаратите са изцяло наша разработка. Предлагаме доживотна гаранция (при определени условия). Оборудвани са с WiFi логер, който позволява дистационен достъп през интернет и регистрира работата на апарата…
НОВО Най-ефективния HHO generator в Европа – Антисмог Генератор Б1 – за автомобили до 4000 кубика.
Ние се борим за чиста природа. Бихме желали всеки българин да постави на автомобила си Водороден генератор с който да намали количеството гориво, което ползва и да подобри екологичните показатели на автомобила си. Апарата е разработен по програма ANTISMOG на кметството на Париж…
Нови Екокатегории
и Екостикери
при Годишен Технически Преглед на автомобилите
В сила от 12 юли 2021г.
Отговаря ли автомобилът ви
на новите
Еко Изисквания?!
Повече от 10 години „HHO България” сме специализирани по отношение екологичността на автомобили с всякакви габарити.
кликнете върху бутона
ЗА НАПЪЛНО БЕЗПЛАТНА КОНСУЛТАЦИЯ
С НАШ СПЕЦИАЛИСТ
Икономия на гориво с Браунов газ
На фона на постоянно растящите цени на горивата, съвсем логично е да търсите начин да спестите пари и икономично да шофирате своя автомобил. Объркани сте в своя избор, защото продукти и технологии с „доказан” ефект не липсват. За сега на световния пазар по ефтино и екологично гориво от водорода не е познато.
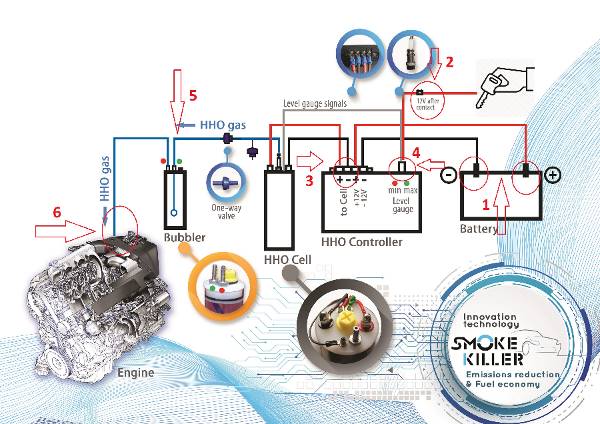
HHO generator и за какво служи?
„ГЕНЕРАТОР НА ГАЗ НА БРАУН” е нова, революционна технология, която:
- Повишава се КПД на ДВГ
- Подобрява се изгарянето на гориво – въздушната смес
- Повишава се въртящия момент на ДВГ 5% – 8%
- В следствие на подобреното изгаряне се намалят до 3 пъти вредните емисии в изгорелите газове.
- Намаля до 3 пъти натрупването на сажди в DPF/FAT и EGR
- Увеличаване до 2 пъти пробега между 2 смени на масло,
- Позволява реализиране на икономия на гориво do 20%,
- Увеличаване живота на двигателя,
- При автомобили с отстранен DPF филтър ниво на вредни емисии като на Евро 5

Намалени вредни емисии, финни
прахови частици и NOx

Икономия на гориво

По-ниски разходи за
поддръжка
Всички водородни генератори които произвеждаме са изцяло наша разработка.
За 11 години сме разработили над 50 различни устройства. Може да израборим всякакво водород базирано оборудване по задание на клиента.
Партньорски сайтове:
Сайт за кога, защо и как се прави Водородно почистване
Сайт на партньорите ни в гр Париж
Пътна Помощ София
Станете дистрибутор
Предлагаме на сервизи, магазини за авточасти или просто хора занимаващи се с автомобили да печелят като монтират или продават Водородните ни генератори. Моля, свържете се с нас на тел. 0878 21 78 10, за да обсъдим условията за съвместна работа.
Организираме курсове за обучение на монтажници на генератори на газ на Браун. За записване на телефон 0878 21 78 10.























